New quicSim PCB SimulationInteractive 3D thermal simulations at your fingertips. Dive in now!
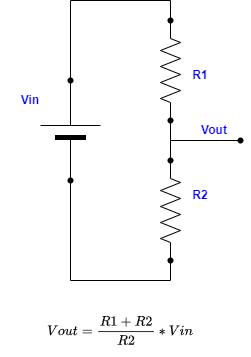
Voltage Divider Calculator
To use this calculator, fill in any three of the four fields (Vin, Vout, R1, R2) and leave the one you want to calculate empty.
Thank You!
We appreciate your feedback.
Working on a complex PCB project?
If our calculator doesn't meet your needs, try our free online PCB simulation for more advanced solutions.
A Beginner's Guide to Voltage Dividers: The Power of Two Resistors
A voltage divider is a fundamental circuit in electronics that produces an output voltage that is a fraction of its input voltage. It's widely used in various applications, such as adjusting the level of a signal, measuring voltages, or providing a reference voltage. This simple yet powerful tool relies on two resistors in series to divide the voltage. The "voltage divider 2 resistors" configuration one of the simplest effective methods for voltage manipulation.
Key Components and Formula
The basic voltage divider circuit consists of two resistors (R1 and R2) connected in series across a voltage supply (Vin). The output voltage (Vout) is taken across the second resistor (R2). The essence of the voltage divider lies in its ability to scale down the input voltage to a lower level, which can be precisely calculated using the voltage divider formula:
Vout = Vin × (R2 / (R1 + R2))
Voltage Divider Rule
The voltage divider rule is a direct application of Ohm's Law and series circuit principles. It states that the output voltage is proportional to the resistance of the second resistor over the total resistance of the circuit. This rule is what makes the voltage divider so useful for creating specific voltage levels from a higher voltage source.
Voltage Divider Calculator
A voltage divider calculator is a handy tool for quickly determining the output voltage of a voltage divider circuit without manual calculations. By inputting the values of Vin, R1, and R2, the calculator provides the Vout value, simplifying the design process for beginners and experienced users alike.
Practical Example: Voltage Divider with 2 Resistors
Consider a voltage divider circuit with Vin = 12V, R1 = 1kΩ, and R2 = 2kΩ. Using the voltage divider formula:
Vout = 12V × (2000 / (1000 + 2000)) = 12V × (2 / 3) = 8V
This result demonstrates how a voltage divider can reduce a 12V input to an 8V output, showcasing the circuit's ability to tailor voltage levels to specific requirements.